Red Light Therapy: The Latest Eczema Treatment?
Eczema is a skin condition that is characterized by redness, inflammation, and itching. It is the most common dermatological condition in the world, affecting approximately 20% of the population. Despite the prevalence of eczema, there is still no cure available.
However, there are many treatment options available that can help reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and improve skin health. One of the treatment options that has been clinically proven effective is red and near-infrared light therapy.
What is Eczema? Symptoms and Causes
Eczema also called atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes itchiness, redness, and inflamed skin. Atopic eczema is the most common type of eczema.
Eczema is a complex disease that is caused by numerous environmental factors, such as stress from different environmental pollutants, immunological factors, including increased serum immunoglobulin-E (lgE) levels and an imbalance of T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th2 cells, and genetic factors.

Although there are many causes, including environmental factors like allergens and pollution, lifestyle choices like stress, and genetics, the exact cause of eczema is still unknown, but red light therapy (RLT) is one type of treatment that shows a promising effect on mitigating the symptoms of eczema.
The symptoms of eczema usually occur in the neck, arm, scalp, and even in the creases of the feet, hands, and elbows.
Effects of Red Light Therapy on Eczema: Proven by Clinical Studies
RLT therapy is said to work by enhancing the mechanisms of skin barrier repair and modulating immune responses.
The Journal of Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine published a study in which light therapy was found to be an effective treatment for atopic dermatitis and thoroughly examined the effect of low-level light therapy on dermatitis symptoms and cytokine changes.
The significant cytokines that are secreted from Th2 include interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-10, which are furthermore involved in humoral immunity, whereas Th1 cells secrete interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-2, which are therefore involved in cellular immunity.
In atopic dermatitis (AD), the levels of IL-4, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) tend to increase, while IFN-γ level tends to decrease. The study employed an LED red light source at 650 nm with an irradiance power of 50 mW/cm^2.
The benefits or alleviating effects of atopic dermatitis can be identified from the following points:
1) Effects of low-level light therapy on the clinical skin severity

In the tracking of 14 days of irradiation, compared with the atopic eczema control group, the red light group showed a significant reduction in scratching and clinical skin severity, as shown in the picture below. All experimental groups exhibit improvements in skin appearance, such as redness level.
2) Effects of low-level light therapy on the genetic expression of IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, and serum IgE
In the study, compared with the AD control group, IL-4 level was significantly decreased in all experimental groups of red light irradiation, whereas there was a remarkable increase in IL-4 concentration compared with the normal control group.
The expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ are also decreased in experimental groups. In addition, the immunoglobulin-E (IgE) analysis in the experimental groups showed a significant decline in the concentration of IgE.
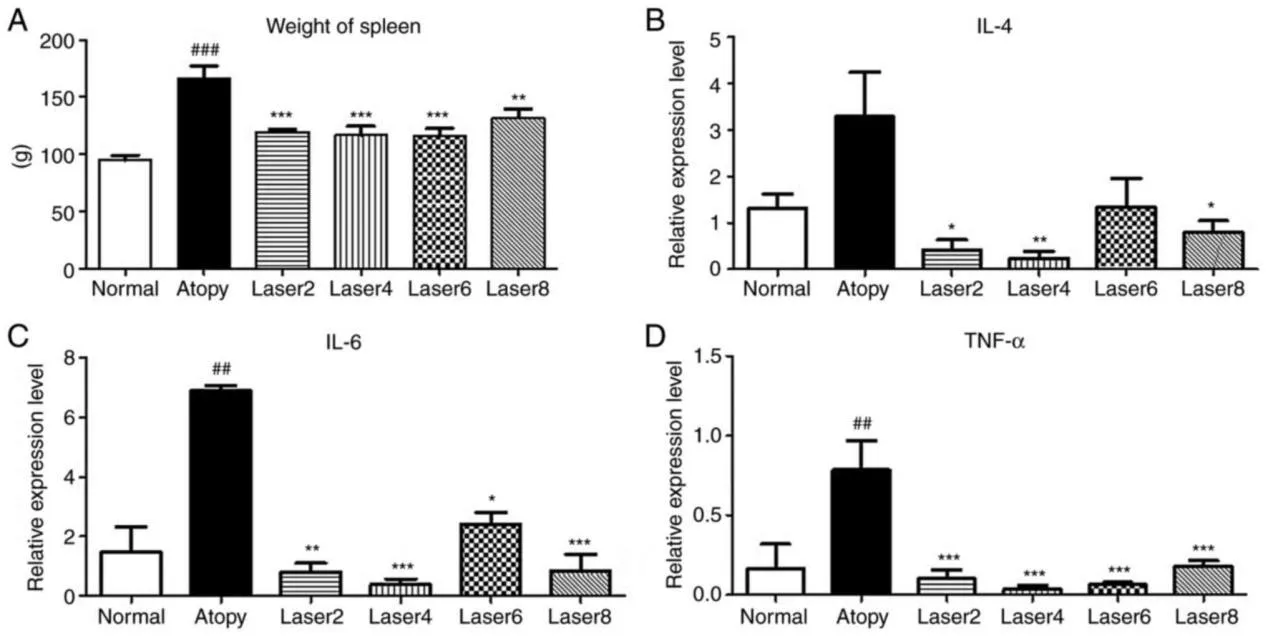
This effect verified that red light therapy can suppress the induction of AD by immunomodulation. Similar effects were able to be demonstrated through the weight of the spleen, where around 40% to 45% of the lymphocytes in the spleen cells are B cells.
Therefore, the increase in spleen weight in the AD group compared with the normal group can be measured as the immune response level.
3) Red and near-infrared light therapy for inflammation
The effect of red light at 650 nm in the study was clinically proven most effective in reducing inflammation, which is one of the influential symptoms of AD. The IgE analysis in this study is also directly related to inflammation level measurement.
The observed improvement in this study didn’t result from the balance of Th1 and Th2 cells but from the intracellular activities induced by red light therapy to recover from inflammation, restore skin conditions, and suppress the genetic expression of certain cytokines.
The anti-inflammatory properties of red light therapy have also been applied to various medical conditions, including arthritis, wound healing, injuries, rosacea, and more.
The combination with UV or near-infrared light therapy?
There are studies that prove the effectiveness of treating eczema with wavelengths in other bands of light. There is one study that proves that using a combination of red and UV lights had a significantly shorter therapeutic treatment time and more improvements than the group using red light therapy alone.
Although they are options, consult with your physician to determine if you need a combinational light. More evidence of phototherapy of UV light for treating eczema can be found in this study.
Similar to red light therapy, using near-infrared light alone is also able to achieve a satisfactory outcome.
This study demonstrated that near-infrared light therapy can also be effective for eczema through the same anti-inflammatory and immunological pathways, which involve the serum levels of IgE and NO and the splenic levels of Th2-mediated cytokines and chemokines.
Choose the right red light therapy device – Bestqool’s advice
While there is no cure for eczema and traditional medications may induce health risks, red light therapy can be a safe alternative to prescriptions.
However, there are many red light therapy devices on the market, so it is important to find one that meets your needs. If you are looking for a red light therapy device for treating eczema, you may need to pay more attention to the following suggestions: